Insect Metamorphosis
Click through the slides below to explore how insects change throughout their lives!
Complete and Incomplete Metamorphosis
Amphibians and many species of invertebrates go through a metamorphosis where they change dramatically in their different phases. However, there are some species of insects that go through an INCOMPLETE metamorphosis!
Let's take a look at what that means.
Complete Metamorphosis
- Has four phases: Egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Change is dramatic between all phases.
- Insects are very active (and hungry) during their larva phase.
- The insect is inactive during the pupa phase.
- Insects cannot reproduce until their adult phase.
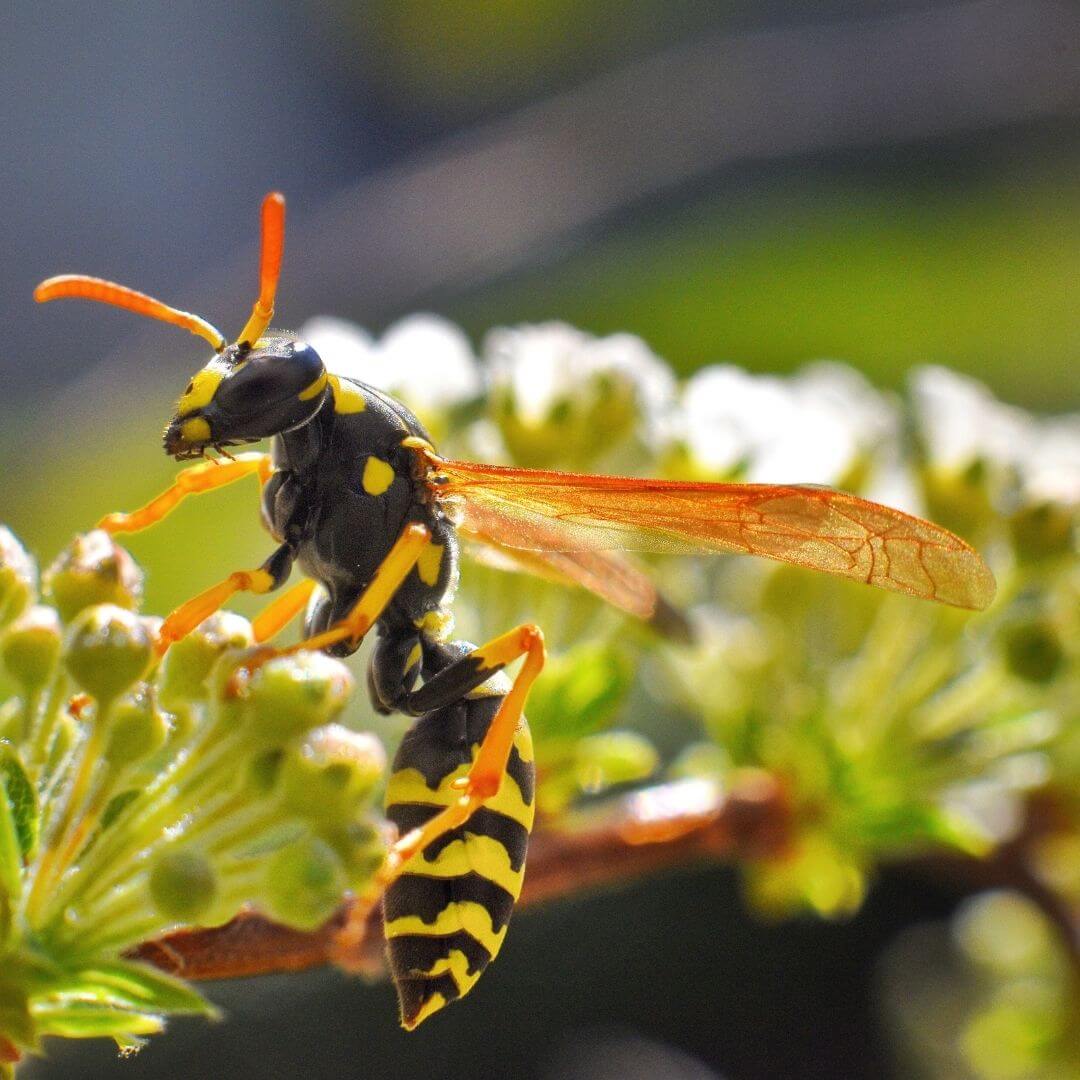
Examples: Butterfly, moth, wasp, ladybug, ant
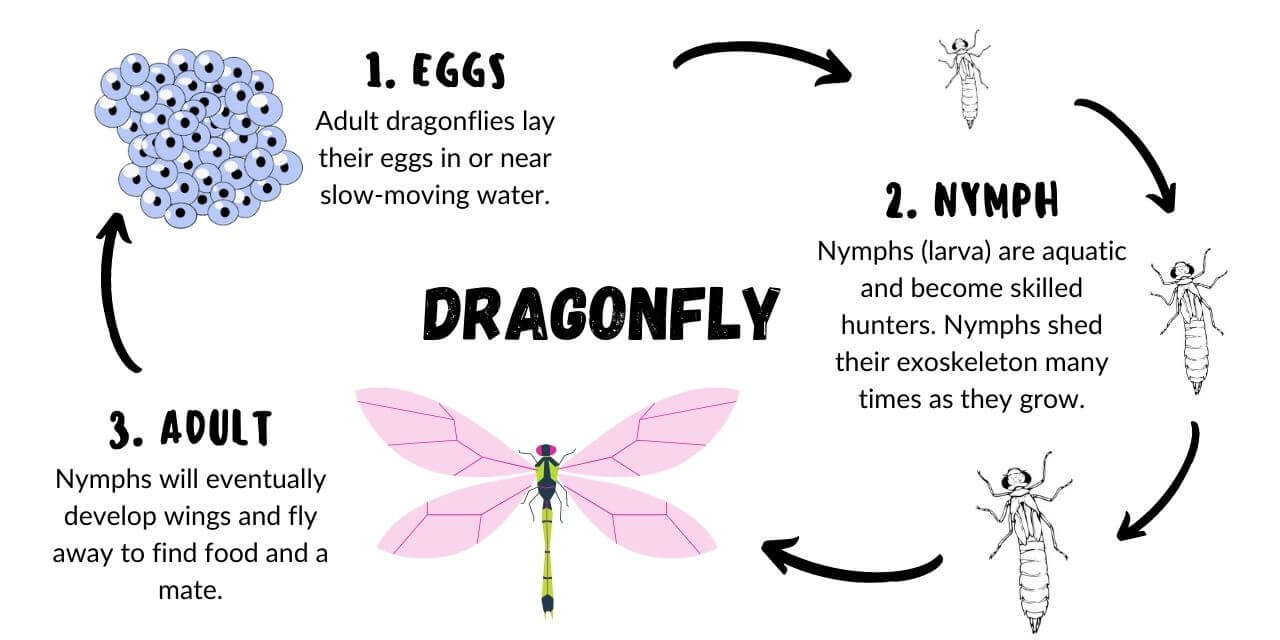
Incomplete Metamorphosis
- Has three phases: Egg, nymph (larva), adult.
- Change is more gradual.
- Nymphs look like small versions of the adult.
- Sometimes, the only difference between the nymph and adult is that adults have wings.
- Nymphs are active and grow slowly.
- Insects can reproduce before reaching adulthood.
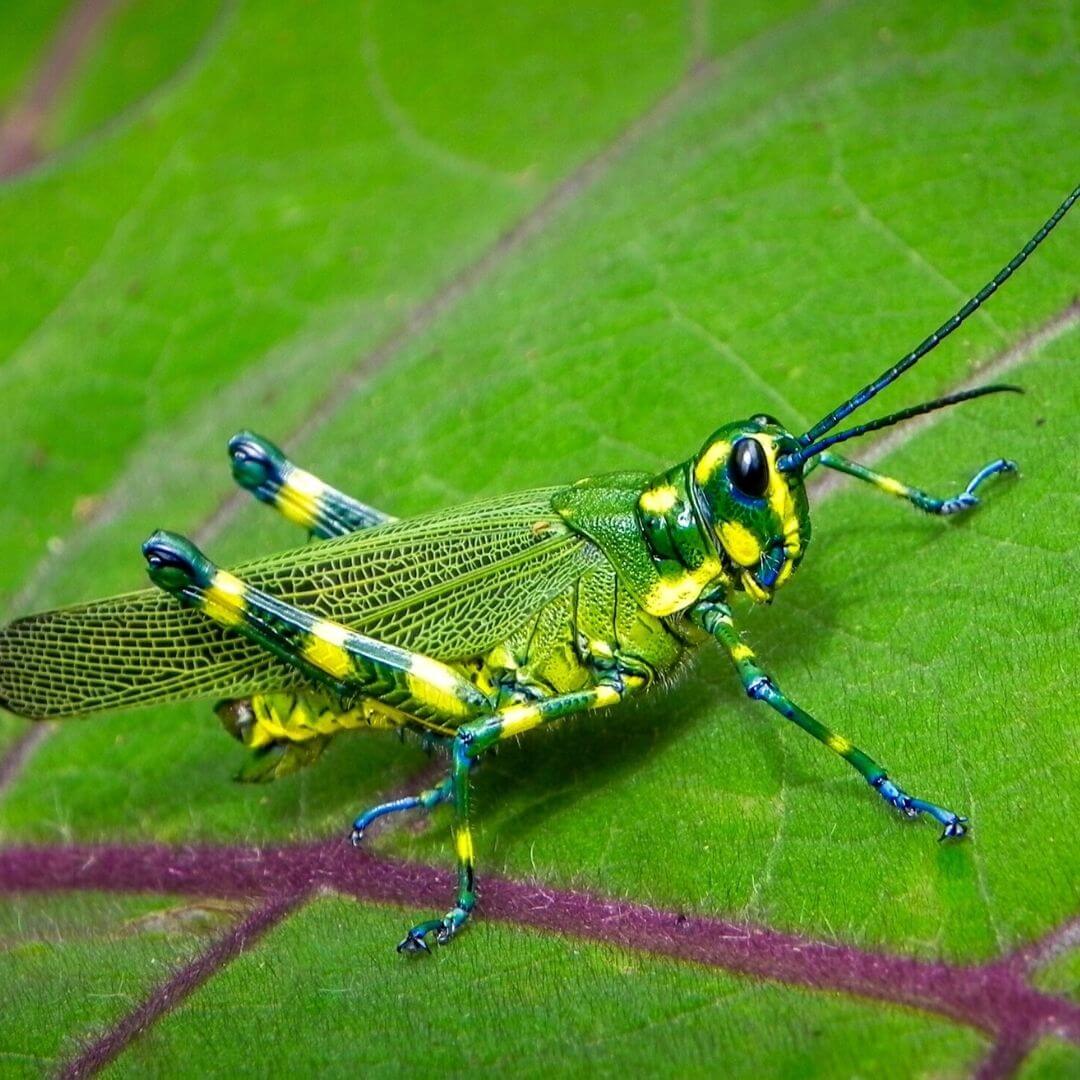
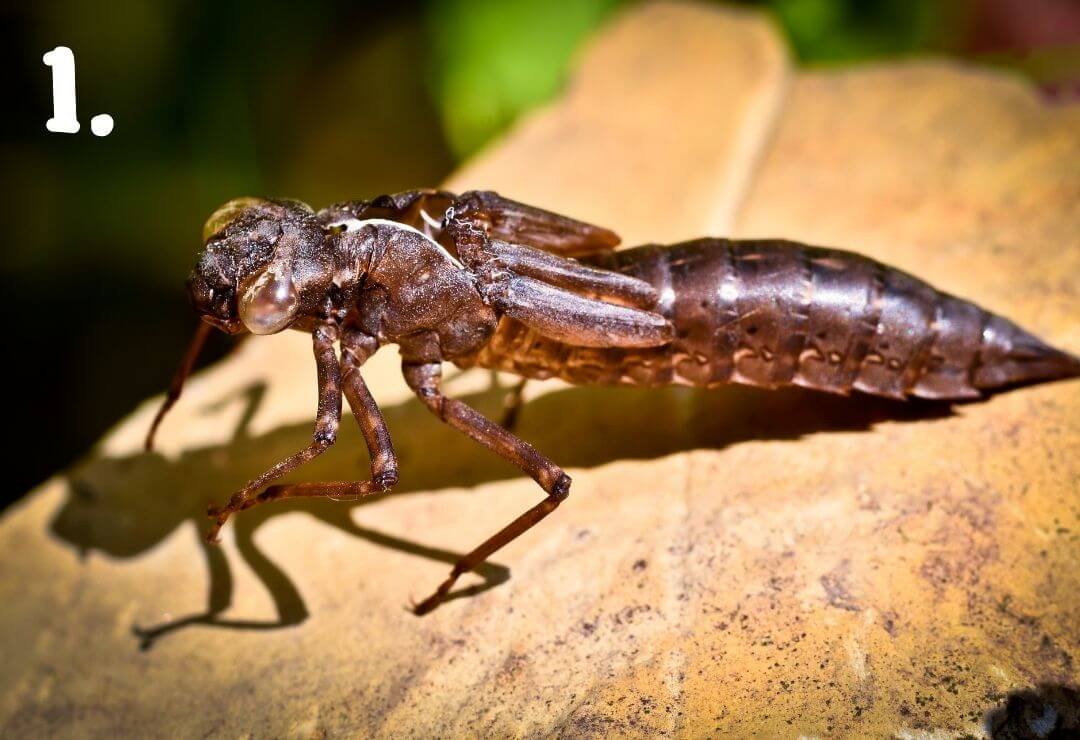
Examples: Dragonfly, grasshopper, praying mantis, cockroach
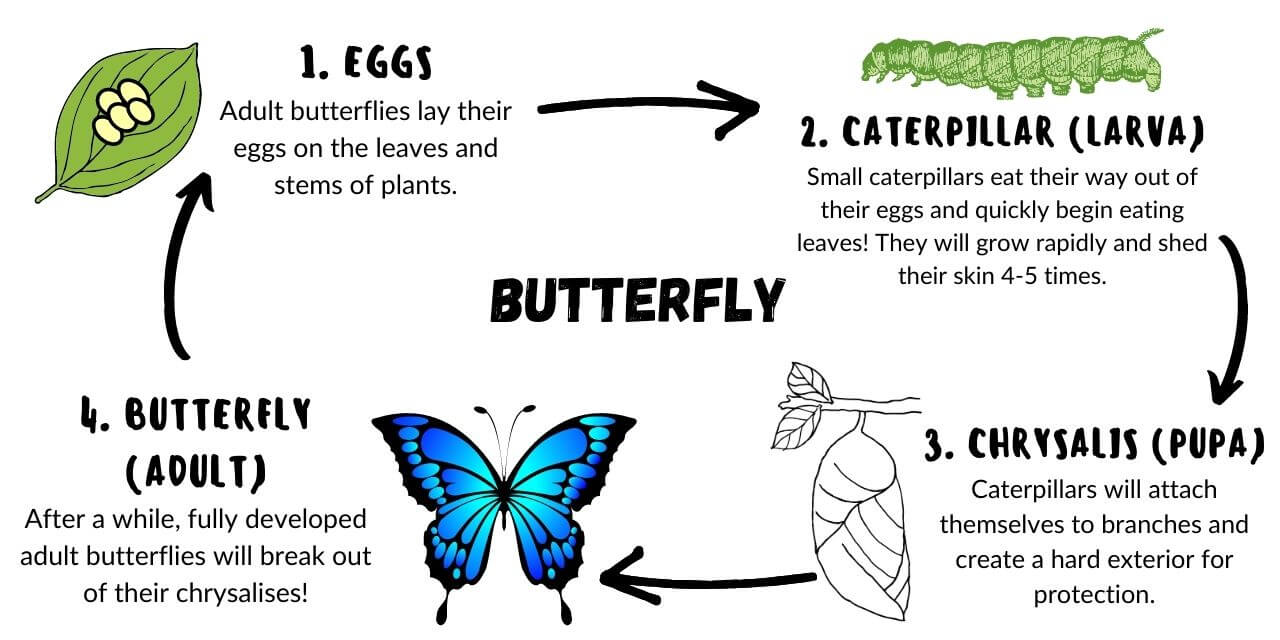
Butterfly Metamorphosis
- Butterflies lay their eggs on the leaves and stems of a host plant! They attach the eggs to the plant using a sticky substance.
- Some butterfly eggs will hatch in just a few weeks, while others won't hatch until the weather gets warmer.
- Once the eggs hatch, the baby caterpillar will eat the host plant for nutrients.
- As a growing caterpillar, they will shed their skin 4-5 times as they outgrow it!
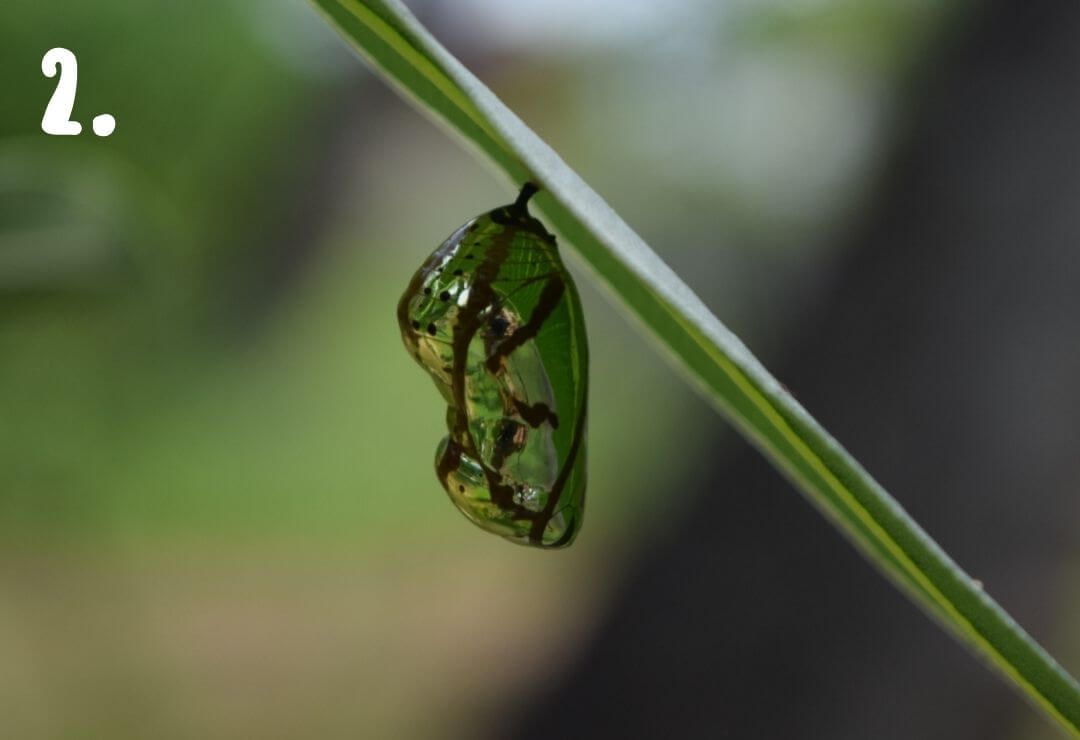
- Once the caterpillar is fully-grown, it will attach itself to a safe spot and develop a hard shell-like coating called a chrysalis.
- After a while of developing inside the chrysalis, an adult butterfly will emerge!
- They must wait for their wings to dry before they can fly off to find nectar.
Why Is Metamorphosis Beneficial?
Avoid Competition
In their larval phase, animals often live in different habitats and eat different food than the adults, which helps them avoid competition!
For example, caterpillars live on plants and eat their leaves, while adults can move from plant to plant and drink nectar!
Avoid Harsh Climate
Some species are strategic about the time of year they lay eggs to start the metamorphosis process. Many short lived species will lay eggs in the spring when there are lots of resources for offspring.
Some other species, like the yucca moth, stay safe in their chrysalis during the cold winter.
Species Specific
Some insects can speed up or slow down the different phases of their metamorphosis depending on the climate.
Some moths and butterflies will remain in their pupas until spring when flowers start to bloom, while many insect eggs can hatch quicker when temperatures are warm.
Metamorphosis Stages
The circles below represent the order for both complete insect metamorphosis and incomplete metamorphosis.
Using the information you just learned, fill in the circles with the appropriate life cycle phase and identify which pathway represents complete metamorphosis and which represents incomplete metamorphosis!
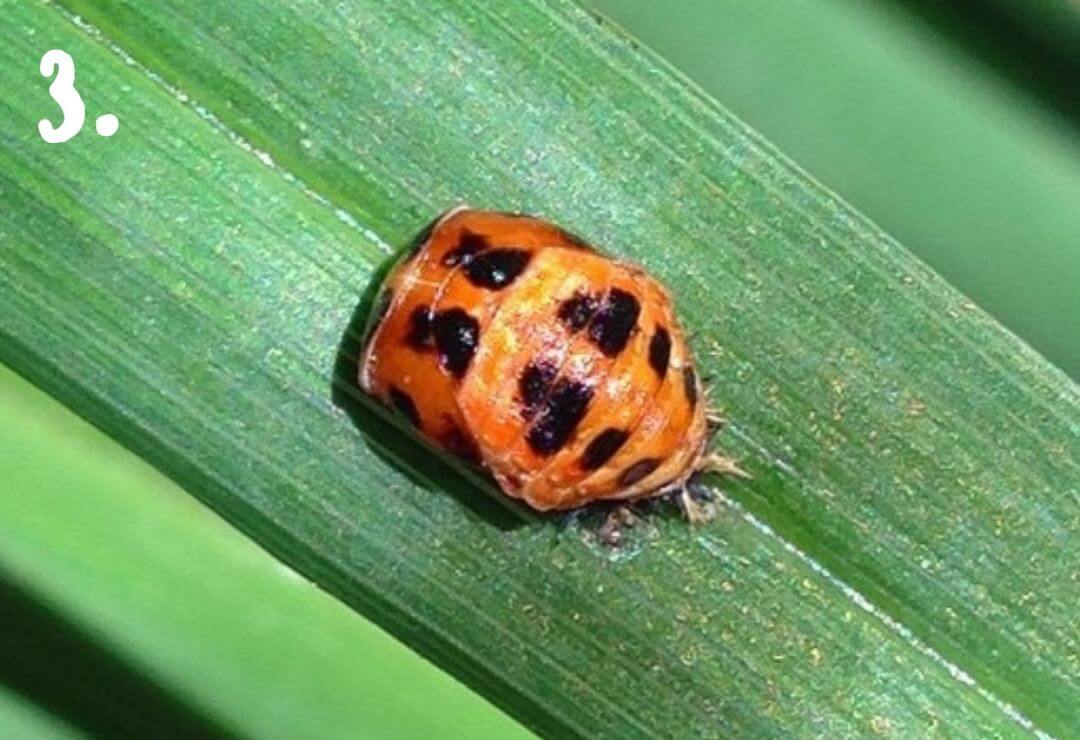
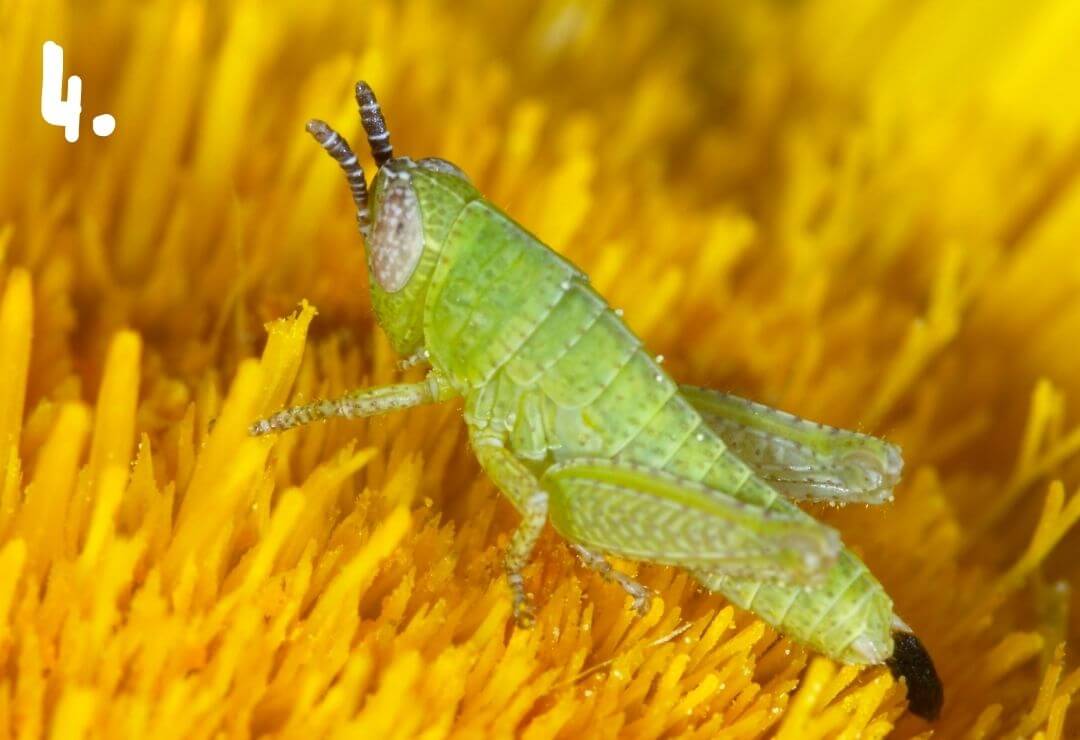
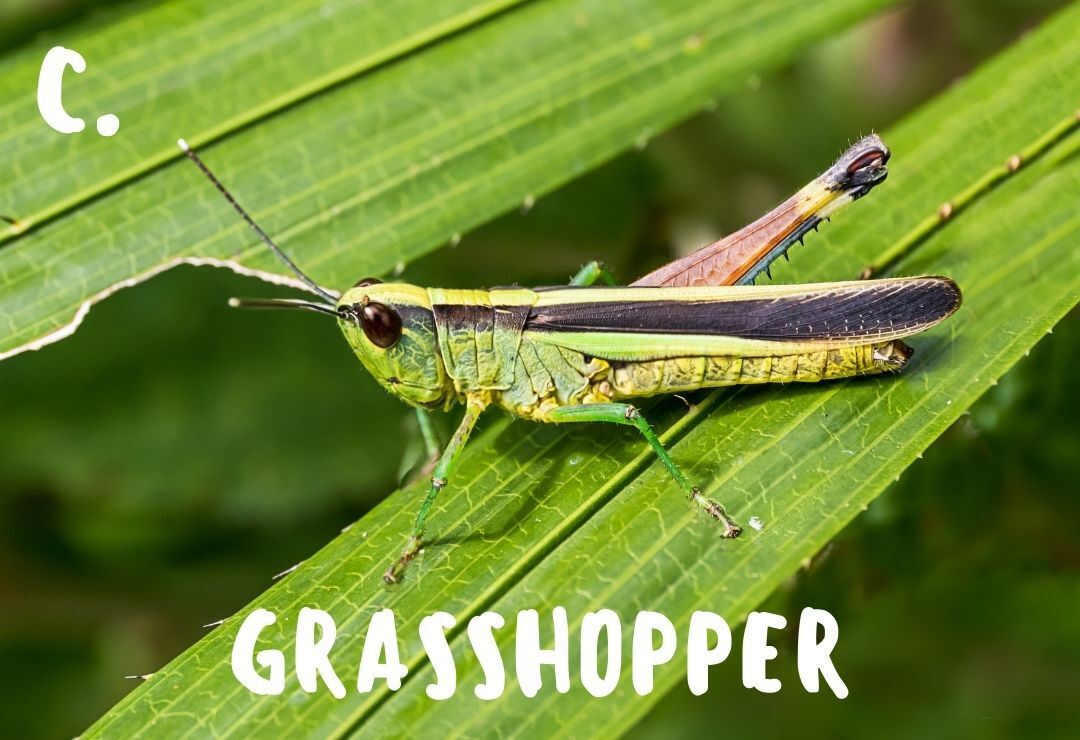
Growing Up!
Animals can look very different during the phases of metamorphosis!
Photos 1 through 4 show four animals during different phases of their metamorphosis. Using your best judgement, match each immature animal to its adult form!
Looking for more amazing lessons?
Check out our EdZOOcating Adventures using the link below!